Efforts to develop drugs can be done by designing drugs. The purpose of drug design is to obtain new drug compounds with better activity and have lower toxicity. Drug design can be done through structural modification. Structural modification is done by synthesizing a number of derivatives of parent compounds, conducting the identification of structures, and conducting the biologic activity test. Before utilizing the in silico test, namely molecular computational testing, the discovery of new drug compounds requires a longer time and greater cost and allows for failure. The method is to synthesize compounds by trial and error, then the activity, pharmacokinetics, and toxicity are determined.
Suko Hardjono, together with Tri Widiandani, Bambang Tri Purwanto and Anindi Lupita Nasyanka in the context of developing new anticancer drugs have predicted activities of N-benzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea and its four derivatives, namely: N-4-chlorobenzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea, N-2,4-dichlorobenzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea, -4-bromobenzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea and N-4-trifluoromethyl-benzoyl-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea, with the target enzyme Sirtuin-1 code on Protein Data Bank (PDB): 4I5I, as a candidate for anticancer drugs. The structure of these compounds can be seen in Figure 1 and Figure 2
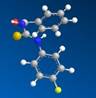
Figure 1. N-benzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea
a) b)
b)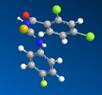 c)
c) d)
d)
Figure 2. Derivatives ofi N-benzoil-N’-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea, which are: a) N-4-chlorobenzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea, b) N-2,4-dichlorobenzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea, c) -4-bromobenzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea and d) N-4-trifluoromethyl-benzoyl-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea
Activity prediction is based on p53 gene function. The p53 gene is found in cancer cells that has a function to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells. The function of the p53 gene will be inhibited by the enzyme Sirtuin-1. In this study, it is expected that the compound which is predicted to have an activity inhibits the work of the Sirtuin-1 enzyme, so that the function of the p53 gene is not disturbed. Predicted results of activities against N-benzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea and its four derivatives is that the five compounds tested have a greater inhibitory activity of the Sirtuin-1 enzyme than hydroxyurea, as one of the anticancer drugs still in use.
In addition to activity predictions, compounds N-benzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea and its four derivatives are also predicted for their pharmacokinetic properties and toxicity. The predicted pharmacokinetic properties are: absorption, metabolism, distribution, and excretion of the drug in the body. From this research, it is found that the five new compounds can be absorbed well in the intestine. All compounds are predicted to have good distribution in tissues except for parent compounds and compounds N -4-trifluoromethyl-benzoyl- N '- (4-fluoro) phenyltiourea. The five compounds do not affect the action of enzymes in the liver which works to eliminate toxins.
Toxicity prediction results show that all compounds do not cause cancer and all compounds are not hepatotoxic (poisoning the liver) except the compound of N-4-trifluoromethyl-benzoyl-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea. From the result of the determination of LD50 in mice (can kill 50% of the number of mice given a test compound), it shows that all compounds have low toxicity.
From the prediction results above it can be concluded that the compound N-4-chlorobenzoil-N'-(4-fluoro)phenyltiourea has good pharmacokinetic properties, which are having the highest activity, does not cause cancer, and is not hepatotoxic, so that the compound is worth synthesizing as a candidate for anticancer drug.
The description above shows the importance of prediction of activity, pharmacokinetic properties, and toxicity before making or synthesizing new drug compounds.
NOTE : Excerpted from the article on:

Journal link: https://search.proquest.com/openview/f5bc10ce655e803e5832c89abb960238/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=1096441








